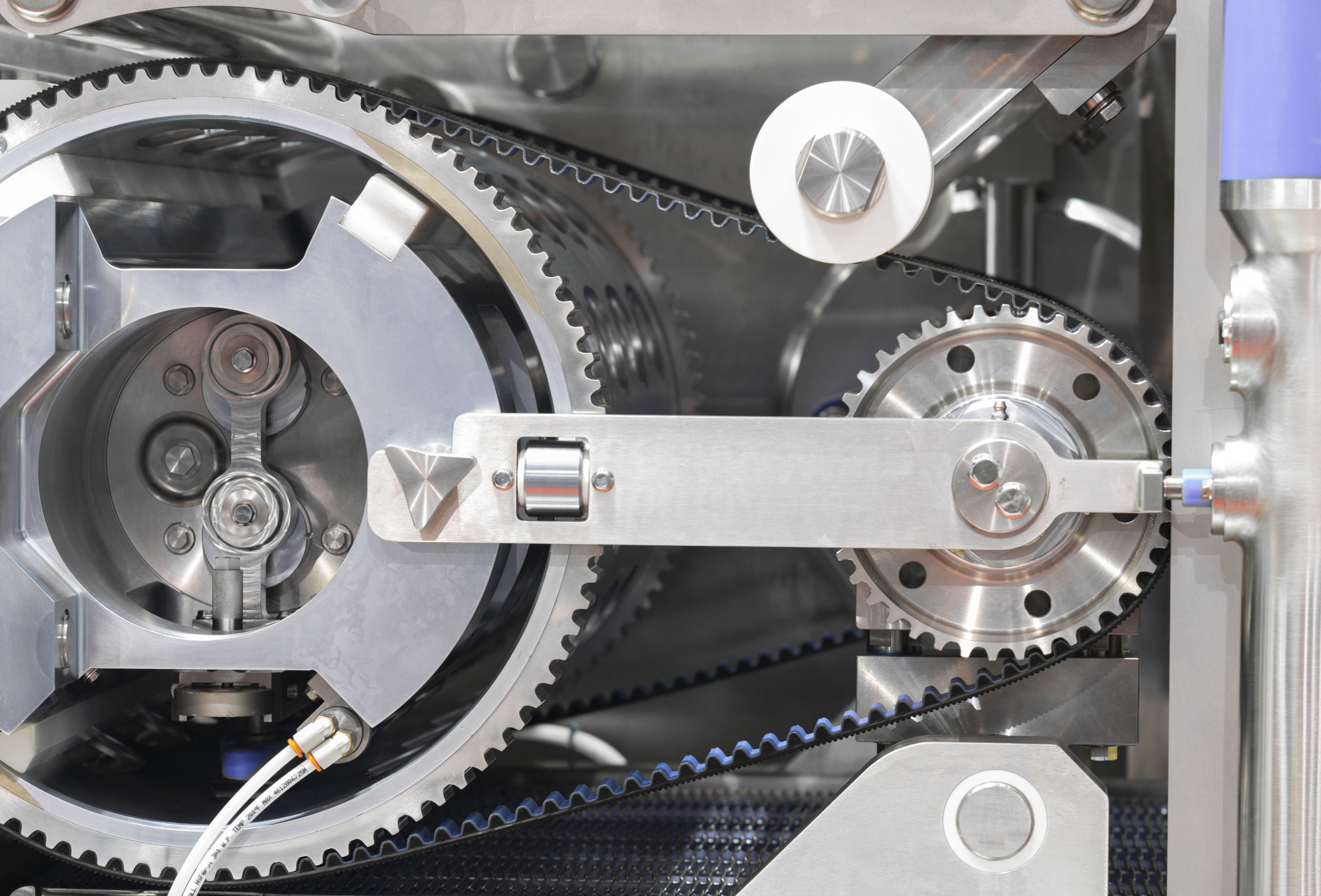
What are timing belts?
Timing belts move in a highly engineered, synchronized fashion. They fall into two categories: Conveying timing belts, which make contact with the product being conveyed, and linear drive timing belts, which activate another piece of equipment in the conveying system without directly touching the product. Both timing belt categories are often used for the final packaging of products across industries.
The ideal material for a timing belt depends on the product being conveyed and whether the belt is a conveying or linear drive timing belt. Standard timing belts are constructed with neoprene or polyurethane, the latter of which is used for food-grade belts or applications needing attachments welded on. The strength member of the timing belt will either be Kevlar®, steel, fiberglass or polyester. Steel is used for timing belts in harsh applications, fiberglass can be punched and polyester can accommodate a smaller pulley radius.
The MIR Belting Audit™ Request
Get a line-by-line itemization of potential ROI for each improvement — at no cost to your facility.
Get startedAdvantages of timing belts
The extreme efficiency of timing belts make them a valuable conveyor system for many plants. The advantages of industrial timing belts include:
Efficiency through positive drive
Timing belts are sprocket-driven (as opposed to tension-driven), meaning the belts won’t shift or break off on the conveyor system and cause tracking issues. This leads to less downtime for maintenance and overall increased efficiency.
Positive indexing for product placement
When plant managers need a packaging line to stop and start at exact times or locations, timing belts can accomplish that. The belt won’t slip or roll, allowing for exact product placement.
Performance synchronization
For parallel application lines running at the same speed, timing belts can move in exact synchronization because they are manufactured in match sets.
Can withstand shock-load starts
Even under conditions where the belt must go from stationary to 60 feet per minute, timing belts can withstand the shock-load start because of their high torque.
Material durability
Timing belts are built to withstand tough operating conditions (there is no stretching or shrinking as with fabric belt styles) which leads to increased belt lifespan.
Customization options
Timing belts complete highly complex jobs and need to be customized precisely for these intricate applications. Our conveyor belting experts begin with confirming your application’s speed, pulley diameters, installation process and number of stops and starts. Then MIR provides customization options that will meet the needs of your conveying system, leading to superior product orientation and synchronization. Customization options for timing belts include:
- Cleats, profiles and V-guides
- Lift-and-transfer modules
- A variety of tooth configurations
- Lateral and longitudinal machining
- Back and edge grinding
- Fabricated cover compounds
- High speeds and accelerations
- Construction to exact dimensional needs
- Accessories such as drives, stoppers and workpieces carriers
- Woven endless or Pin-Lock spliced
Considerations for timing belts
It is often pre-determined in plants which application lines will run timing belts. Regardless, it is important for plant managers to keep the installation and changeout time for timing belts in mind, as it takes much longer than a fabric belt system. This can be remediated with a Pin-Lok splice (instead of an endlessly woven belt) that is easier to take on and off the conveyor system.
Another consideration for timing belts is their size limitations. Most belt product styles can be manufactured to nearly any size, but the mandrel fabrication method of timing belts limits their size.
For these highly engineered products, collaborating closely with a belting supplier will yield a best-fit timing belt for your application line. Get a quote from a belting expert today.
 View Locations
View Locations 24/7 Service: 877-MIR-BELT (877-647-2358)
24/7 Service: 877-MIR-BELT (877-647-2358)





 Intro
Intro